In Cameroon, outdated health accounts impeded informed decision-making and policy development, and high out-of-pocket costs indicated a need for more equitable healthcare financing.[1] The update of these accounts was crucial for Cameroon to effectively implement its national health insurance, Couverture Santé Universelle (CSU), which aims to provide quality healthcare for all by minimizing financial barriers. Recognizing the urgency, the World Health Organization (WHO) intervened with a comprehensive support strategy, providing technical assistance to strengthen Cameroon's economic monitoring capacity. This support enabled Cameroon to update its Health Accounts for 2018-2019, the first such update since 2011. The current data reveals a decrease in the health budget's proportion and an increase in out-of-pocket health expenses, signaling a trend towards greater personal financial responsibility for healthcare costs - a shift that could impede healthcare access. This essential evidence is vital for the Ministry of Public Health to shape policies and advocate for investments that enhance financial protection. WHO’s 13th General Programme of Work (GPW13) prioritizes achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC), focusing on enhancing financial protection through the 2020-2025 biennial budget programs. These programs support the implementation of Cameroon's 2020-2030 Health Sector Strategy, specifically in health system strengthening. WHO Cameroon has therefore supported the Ministry of Public Health in reactivating Cameroon’s health accounts to enable the production, analysis, and use of health expenditure data to improve access to quality essential health services.
WHO's Key Contributions
- Providing an international consultant for technical guidance during the NHA production process.
- Securing funding with partners like UNICEF and GIZ for the initiative.
- Organizing the official launch of NHA production process by the Minister of Health himself.
- Establishing and training the NHA national focal point and multisectoral technical team using the System of Health Accounts 2011 (SHA 2011).
- Offering expertise in formulating the data collection tool, overseeing data collection, and validating the NHA report.
- Presenting the report to key policymakers and advocating for its utilization in revising the national health financing strategy and National Health Insurance implementation.
How did Cameroon, with the support of WHO, achieve this?
The health accounts system is an international accounting framework that systematically monitors health expenditure, allowing economies to be described through comparable accounts across nations. Trends in health spending and its components are crucial for shaping policies and investments to align health systems with public needs, improving system performance, and ensuring transparency and accountability.[2] In July 2020, Cameroon's Minister of Public Health formally initiated the National Health Accounts (NHA) production process. Acknowledging the significance of this project, WHO Cameroon deployed a WHO international consultant to offer technical guidance. Additionally, WHO Cameroon secured funding in collaboration with partners like the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) and the German Development Cooperation (GIZ), further bolstering this vital initiative.
To ensure the project's success, WHO organized the official launch of the process by the Minister of Public Health. WHO then focused on enhancing national expertise in producing National Health Accounts (NHA). A multisectoral technical team was established and a NHA national focal point was appointed by the Minister of Public Health. WHO then trained this team using the global System of Health Accounts 2011 (SHA 2011) framework, which facilitates tracking health expenditure flows from sources to uses.[3]
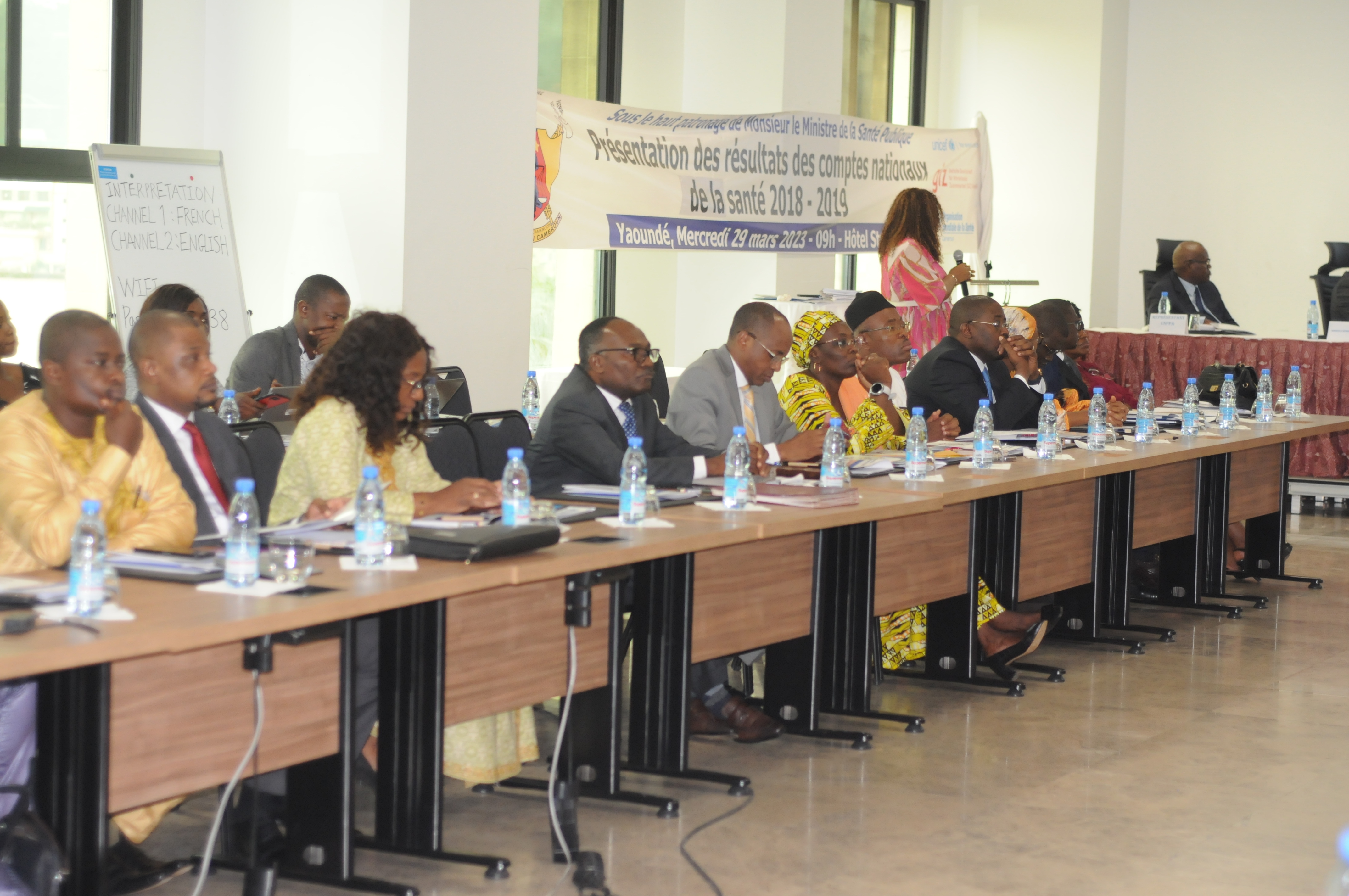

Mrs Joelle Bouba, Director of the Department of Financial Resources and Property, from the Ministry of Health discusses 2018-2019 health accounts findings at a key meeting in Yaoundé, Cameroon on 29 March 2023.
Photo credit: WHO Cameroon/Barbara Etoa
WHO also played a critical role in ensuring the quality of NHA data. WHO provided technical support to develop a data collection tool, oversaw data collection, scrutinized the collated information, thoroughly reviewed the compiled data, and validated the NHA report. This involved the 3 levels of WHO (Country Office, Regional Office and headquarters).
This report, a key result of these efforts, was presented to key policymakers in May 2023, including the Minister of Health, representatives from various sectoral ministries, civil society, and partners. WHO strongly advised using this new data to update the national health financing strategy and to inform critical decisions, such as the implementation of National Health Insurance. Additionally, WHO is preparing a policy brief to extend the use and impact of this data.
The 2018-2019 National Health Accounts provided pivotal insights into the patterns of healthcare financing and expenditure within the country. First, it was observed that the State's budget allocation for healthcare remained consistently low, averaging below five percent, which falls significantly short of the Abuja target that recommends fifteen percent of the budget be dedicated to healthcare. Second, the findings underscored that households emerged as the principal contributors to healthcare expenses during this timeframe, with out-of-pocket payments accounting for 72 percent of the total current healthcare expenditure. Third, an analysis revealed that more than 53 percent of household health spending was allocated to the purchase of pharmaceutical products outside health facilities, highlighting a considerable dependence on out-of-pocket expenditures for medication.
“The National health account highlights that access to good quality medicines is a strategic issue to achieve Universal Health Coverage in Cameroon.”
Dr Phanuel Habimana, WHO Representative for Cameroon
As a result of these collective efforts, Cameroon now has a detailed record of the primary expenditure channels and the entities responsible for them. The Director of the Department of Financial Resources and Property in Cameroon’s Ministry of Health, Mrs Joelle Bouba, highlighted the data's value, noting that “following the publication of the health accounts, the Ministry of Planning is more attentive to the budgetary requests of the Ministry of Health.”
“With the results of the health accounts, we are more aware of the efforts that need to be made to move towards universal health coverage.”
- Dr Désiré Mintop, Coordinator of the National Technical Committee on Universal Health Coverage, Cameroon
The updated health accounts enable informed decision-making which is anticipated to increase healthcare investment through refinement of the national health financing strategy and ensure the financial protection of the Cameroonian public through the evidence-informed roll-out of National Health Insurance. Efforts are under way to develop NHA for 2020-2021 and institutionalise this process in partnership with the National Institute of Statistics.
- World Health Organization. Health accounts [web portal]. Health Accounts WHO, accessed 1 February 2024.
- World Health Organization. A system of health accounts 2011 [publication]. A System of Health Accounts 2011, accessed 1 February 2024.
- Republic of Cameroon. Plan National de Développement Sanitaire 2021-2025.