EPI is one of the most successful public health programs in the country. Despite the tremendous success, there is still zero dose and under- immunized children in high- risk and hard- to- reach areas. One of the priority objectives of immunization is to identify and reach zero doses and under- immunized children and missed communities. To strengthen the immunization system regarding mapping, microplanning, supervision, and monitoring, WHO proposed national EPI to introduce innovative technology like geographical information system (GIS) in the EPI program. GIS provides the highest possible support in mapping equitable distribution of the vaccination sites, disease outbreaks, and trends with accurate geospatial data in context to catchment area, such as high- risk and hard- to- reach, slum population, distance from health facility to service delivery point, etc. The technology can enable EPI program planning, monitoring, and decision- making in an effective way.
.jpg?sfvrsn=5c803696_2)
A group of audience in the event. Photo credit: WHO/Md Fozle Azim
National EPI selected multiple areas to introduce the innovative initiative. WHO Bangladesh Country office and WHO HQ GIS team, in collaboration with National EPI and MIS, DGHS is implementing this activity. WHO-IVD network and other relevant departments of the WHO were trained on the ArcGIS tool. This training will help to enrich knowledge and skills for prompt decision- making and programmatic interventions where and when applicable, particularly in events of public health importance.
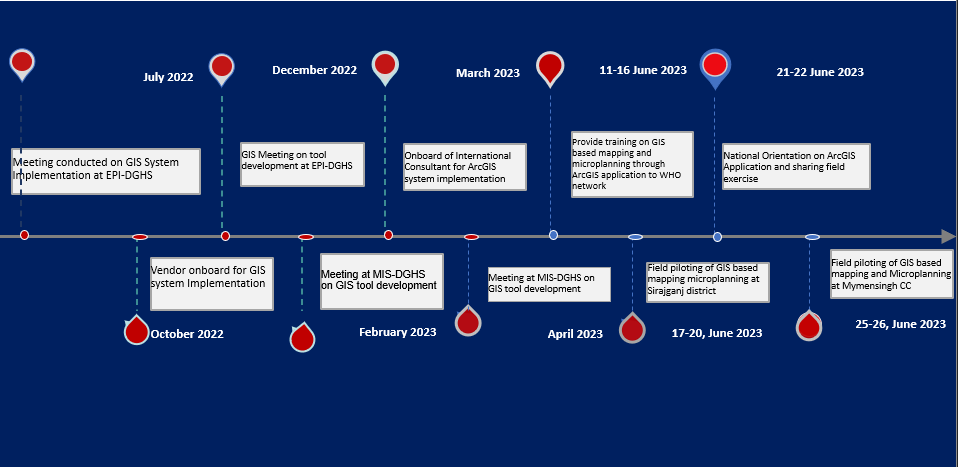
Roadmap towards GIS introduction in EPI program
The GIS-based mapping and microplanning initiative was successfully implemented in Sirajganj Sadar Upazila and Mymensingh City Corporation. Health Managers and relevant field staff received comprehensive training on GIS-based mapping and microplanning using ArcGIS. A workshop was conducted to prepare the base map for digital microplanning. Additionally, a national level orientation session was held to share the field experience gained from the piloted areas. By the end of 2023, the GIS-based mapping and microplanning project aims to be scaled up in at least eight districts and four city corporations. For more information about the web story please contact ssultana@who.int
