Programmes
Joint programmes
Access Initiative for Quitting Tobacco
In response to last year’s ECOSOC resolution, the UN Inter-Agency Task Force has led the efforts to create the Access Initiative for Quitting Tobacco (AIQT), a multi stakeholder initiative to help smokers quit tobacco. The initiative gives people free access to nicotine replacement therapy and to Florence, a digital health worker based on artificial intelligence that dispels myths around COVID-19 and tobacco and helps people develop a personalized plan to quit tobacco. AIQT is the first project developed in response to the ECOSOC call upon the Task Force to scale-up access to NCD diagnostics, treatment and care to provision with safe, effective, quality and affordable essential medicines for all, as well as to promote health technologies for stronger health systems, including regulatory frameworks and good supply chain management.
Catalyzing action on NCDs
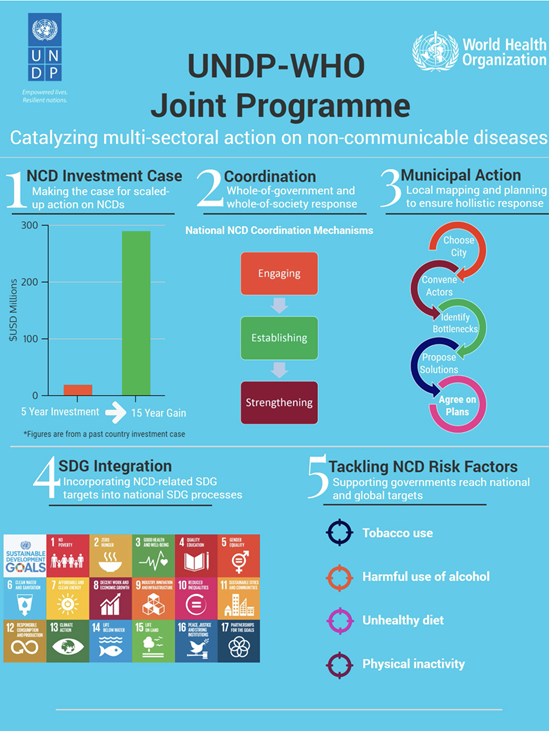
The UNDP WHO Joint Programme on NCDs (Joint Programme) will support countries to develop effective national multisectoral noncommunicable diseases (NCD) responses to achieve the NCD-related targets in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and other global commitments. The Joint Programme stems from the recognition that reducing the burden of NCDs cannot be achieved by the health sector alone and requires action across a number of sectors. The Joint Programme will strengthen whole-of-government and whole-of-society responses to NCDs in up to 24 countries.
SAFER: Preventing and reducing alcohol-related harms

WHO has released SAFER, a new initiative and technical package outlining 5 high-impact strategies that can help governments to reduce the harmful use of alcohol and related health, social and economic consequences. SAFER is the newest WHO-led roadmap to support governments in taking practical steps to accelerate progress on health, beat noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) through addressing the harmful use of alcohol, and achieve development targets.
Global Regulatory and Fiscal Capacity Building Programme: promoting healthy diets and physical activity

2014 IDLO signed agreements with WHO and the Caribbean Public Health Agency (CARPHA) to build legal capacity to address public health challenges. The initial focus is on obesity, diabetes, healthy diets and physical activity. Also in 2014, IDLO, the WHO and the University of Sydney convened the first regional consultation on overweight, obesity, diabetes and law in the Western Pacific. IDLO will support further regional consultations and national capacity building of government, academic and civil society partners to strengthen national legal frameworks and capacity to address NCDs. Programs will be tailored to regional and national needs.
FCTC2030: strengthening WHO FCTC implementation to achieve the SDGs

Tobacco is a major public health concern and a barrier to development around the world. The FCTC 2030 project is strengthening tobacco control in low- and middle-income countries through promoting and supporting governments to accelerate the implementation of the WHO FCTC.
UN Joint Action on Cervical Cancer

Each year, over a quarter of a million women die of cervical cancer: 90% of these deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries. Scaling-up existing effective tools for prevention and control – particularly vaccinating against the human papilloma virus and screening for and treating pre-cancerous cervical lesions – can prevent most of these deaths. In 2016, seven UN agencies established a new five-year Joint Global Programme on Cervical Cancer Prevention and Control to elimination of cervical cancer as a public health concern across the world, bringing together the strengths of their work to protect and promote the health of women and girls.
MoU and joint programming document
60th IAEA General Conference side event
New United Nations joint global programme to prevent cervical cancer
Partners roundtable hosted by the US Government
ITU-WHO Mobile Health for NCDs Initiative

WHO and the International Telecommunications Union are collaborating with a range of Members States and other partners in a ground breaking initiative, which focuses on the use of mobile technologies to improve the prevention and treatment of NCDs. This partnership aims to contribute to global and national efforts to save lives, minimize illness and disability, and reduce the social and economic burden that NCDs create. The ITU-WHO mHealth initiative is harnessing the best available mobile technology, making mHealth accessible to all countries as a powerful anti- NCD measure.
UNODC-WHO-UICC Joint Global Programme on access to controlled drugs for medical purposes while preventing diversion and abuse

The Joint Global Programme is a partnership between the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNDOC), World Health Organization (WHO) and the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC). The objective is to lead a coordinated worldwide response to improve access to controlled drugs for medical purposes, while controlling for abuse and diversion, therefore increasing the number of patients globally receiving appropriate treatment.
Access to controlled drugs for medical purposes, while preventing diversion and abuse (GLOK67)
UNODC-WHO Joint Programme for Drug Dependence Treatment and Care

The Joint Programme on Drug Dependence Treatment and Care is a collaboration between UNODC and WHO. The aim is to support the development of comprehensive, integrated health-based approaches to drug policies that can reduce demand for illicit substances, relieve suffering and decrease drug-related harm to individuals, families, communities and societies.
UNODC and WHO launch joint drug dependence treatment programme
MoU UNODC –WHO
Working Groups
- Thematic Working Group on Nutrition
Terms of Reference - Thematic Working Group on NCDs and Environment
Terms of Reference - Thematic Working Group on NCDs and Environment
Action plan - Thematic Working Group on Mental Health
Terms of Reference - Thematic Working Group on Physical Activity
Terms of Reference - Thematic Working Group on Tobacco Control
Terms of Reference
Joint letters and agreements
- IDLO and WHO - December 2014
- Joint working memo - March 2014, UNDP, WHO and World Bank
- Second UNDP/WHO letter - February 2014, Integrating NCDs into UNDAFs
- UNAIDS-WHO Letter of Agreement - July 2012
- First UNDP/WHO letter - March 2012, Integrating NCDs into UNDAFs
- Joint programme on cancer control - March 2009 Arrangements between IAEA and WHO