The WHO Programme for International Drug Monitoring
Pharmacovigilance (PV) is defined as the science and activities relating to the detection, assessment, understanding and prevention of adverse effects or any other drug-related problem.
The aims of PV are to enhance patient care and patient safety in relation to the use of medicinal products; and to support public health programmes by providing reliable, balanced information to assess the risk-benefit profile of medicines.
In 1963, during the 16th World Health Assembly, resolution 16.36 called for “a systematic collection of information on serious adverse drug reactions during the development and particularly after medicines have been made available for public use”. This led to the formation of the WHO Programme for International Drug Monitoring (PIDM) in 1968.
WHO PIDM Members submit reports of adverse reactions associated with medicinal products, known as Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSRs) to the WHO global database, VigiBase. VigiBase is managed and maintained by the WHO Collaborating Centre for International Drug Monitoring, known as Uppsala Monitoring Centre. In July 2023, there were over 35 million reports of adverse reactions in VigiBase. Data in VigiBase are recorded in a structured and comprehensive way to allow the detection of potential medicinal safety hazards.
In April 2015, WHO launched VigiAccess. VigiAccess is a new web application that will allow anyone to access information and encourage the reporting of adverse effects from medicinal products.
New Members of the WHO Programme for International Drug Monitoring
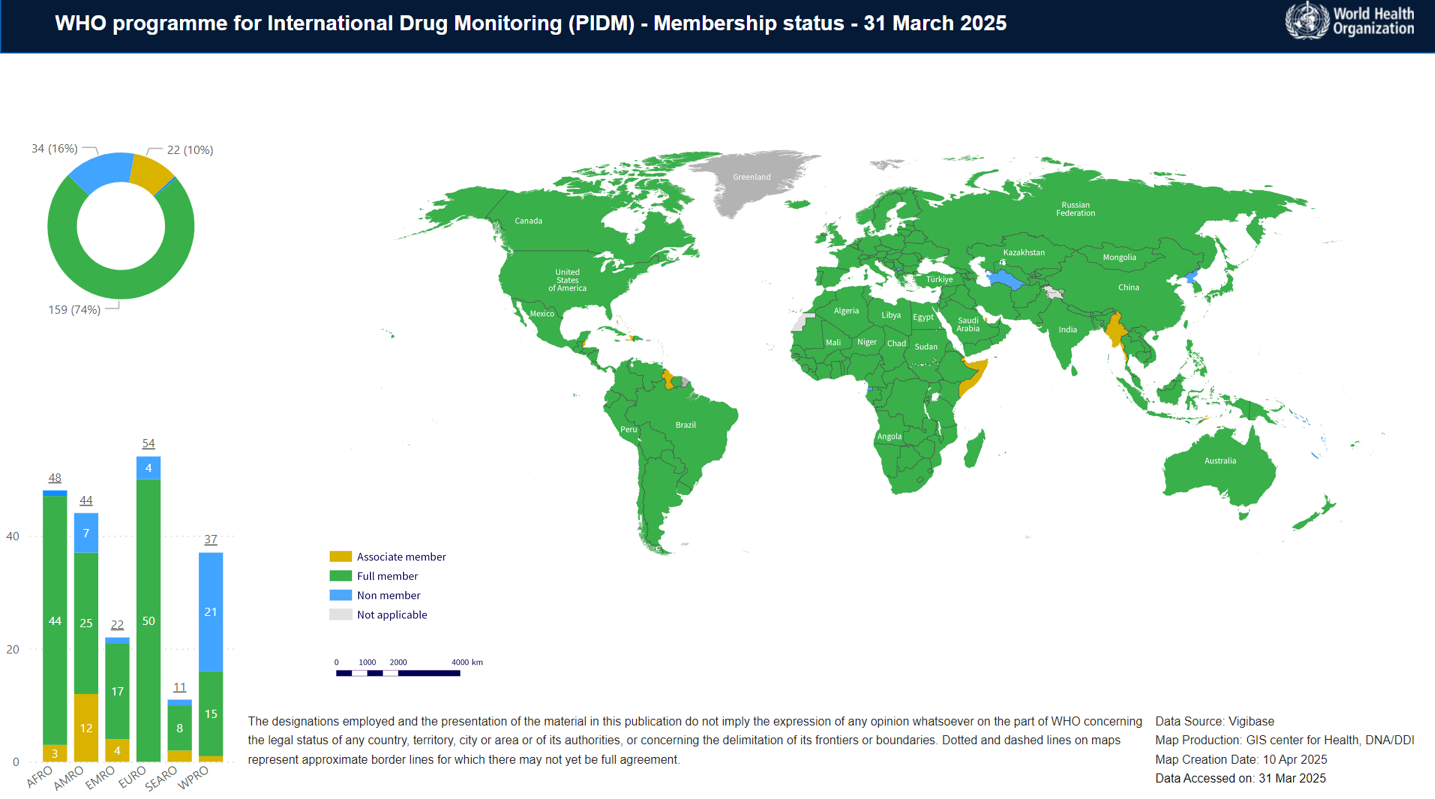
We have welcomed Sao Tome and Principe as full member of our big family of pharmacovigilance (medicine & vaccine safety), the WHO Programme for International Drug Monitoring (PIDM), following their successful safety reports sharing with the WHO VigiBase. The WHO PIDM has now 160 full members & 22 associate members. Information as of 21 March 2025.
Map showing the members of the WHO PIDM as of March 2025. Green: Full member; Orange:
Associate member; Blue: Non-member.
Full and associate members of the WHO PIDM (year they joined)
Full member countries (160)
WHO member states
Afghanistan (2016)
Albania (2020)
Algeria (2021)
Andorra (2008)
Angola (2013)
Argentina (1994)
Armenia (2001)
Australia (1968)
Austria (1991)
Azerbaijan (2018)
Bangladesh (2014)
Barbados (2008)
Belarus (2006)
Belgium (1977)
Benin (2011)
Bhutan (2014)
Bolivia (Plurinational State of) (2013)
Bosnia and Herzegovina (2019)
Botswana (2009)
Brazil (2001)
Brunei Darussalam (2005)
Bulgaria (1975)
Burkina Faso (2010)
Burundi (2022)
Cabo Verde (2012)
Cambodia (2012)
Cameroon (2010)
Canada (1968)
Central African Republic (2022)
Chad (2018)
Chile (1996)
China (1998)
Colombia (2004)
Congo (2021)
Costa Rica (1991)
Côte d'Ivoire (2010)
Croatia (1992)
Cuba (1994)
Cyprus (2000)
Czechia (1992)
Democratic Republic of the Congo (2010)
Denmark (1971)
Dominican Republic (2020)
Ecuador (2017)
Egypt (2001)
El Salvador (2017)
Eritrea (2012)
Estonia (1998)
Eswatini (2015)
Ethiopia (2008)
Fiji (1999)
Finland (1974)
France (1986)
Gabon (2023)
Gambia (2021)
Georgia (2018)
Germany (1968)
Ghana (2001)
Greece (1990)
Guatemala (2002)
Guinea (2013)
Guinea-Bissau (2022)
Honduras (2020)
Hungary (1990)
Iceland (1990)
India (1998)
Indonesia (1990)
Iran (Islamic Republic of) (1998)
Iraq (2010)
Ireland (1968)
Israel (1973)
Italy (1975)
Jamaica (2012)
Japan (1972)
Jordan (2002)
Kazakhstan (2008)
Kenya (2010)
Kuwait (2021)
Kyrgyzstan (2003)
Lao People’s Democratic Republic (2015)
Latvia (2002)
Lebanon (2021)
Lesotho (2024)
Liberia (2013)
Libya (2021)
Lithuania (2005)
Luxembourg (2020)
Madagascar (2009)
Malawi (2019)
Malaysia (1990)
Maldives (2016)
Mali (2011)
Malta (2004)
Mauritania (2023)
Mauritius (2014)
Mexico (1999)
Mongolia (2021)
Montenegro (2009)
Morocco (1992)
Mozambique (2005)
Namibia (2008)
Nepal (2006)
Netherlands (1968)
New Zealand (1968)
Nicaragua (2020)
Niger (2012)
Nigeria (2004)
North Macedonia (2000)
Norway (1971)
Oman (1995)
Pakistan (2018)
Panama (2016)
Papua New Guinea (2018)
Paraguay (2018)
Peru (2002)
Philippines (1995)
Poland (1972)
Portugal (1993)
Republic of Korea (1992)
Republic of Moldova (2003)
Romania (1976)
Russian Federation (1998)
Rwanda (2013)
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines (2020)
Sao Tome and Principe (2025)
Saudi Arabia (2009)
Senegal (2009)
Serbia (2000)
Sierra Leone (2008)
Singapore (1993)
Slovakia (1993)
Slovenia (2010)
South Africa (1992)
South Sudan (2024)
Spain (1984)
Sri Lanka (2000)
Sudan (2008)
Suriname (2007)
Sweden (1968)
Switzerland (1991)
Syrian Arab Republic (2018)
Tajikistan (2023)
Thailand (1984)
Togo (2007)
Tunisia (1993)
Türkiye (1987)
Uganda (2007)
Ukraine (2002)
United Arab Emirates (2013)
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (1968)
United Republic of Tanzania
Mainland (1993)
Zanzibar (2024)
United States of America (1968)
Uruguay (2001)
Uzbekistan (2006)
Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of) (1995)
Viet Nam (1999)
Yemen (2022)
Zambia (2010)
Zimbabwe (1998)
Associate members (22)
WHO member states
Antigua and Barbuda
Bahamas
Bahrain
Belize
Comoros
Cook Islands
Djibouti
Dominica
Equatorial Guinea
Grenada
Guyana
Haiti
Myanmar
Qatar
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Seychelles
Somalia
Timor-Leste
Territories /Areas
Anguilla
British Virgin Islands
Montserrat
Recommendations

Recommendations from the 40th Annual Meeting, Kampala 2017
The working group discussed the scope and limits of pharmacovigilance (PV) centres in preventing medication errors and how PV centres can have proactive...

Recommendations from the 39th Annual Meeting, Muscat 2016
The working group discussed the scope and limits of pharmacovigilance (PV) centres in preventing medication errors and how PV centres can have proactive...

Recommendations from the 38th Annual Meeting, New Delhi 2015
The working group discussed the scope and limits of pharmacovigilance (PV) centres in preventing medication errors and how PV centres can have proactive...

Recommendations from the 37th Annual Meeting, Tianjin 2014
The working group discussed the scope and limits of pharmacovigilance (PV) centres in preventing medication errors and how PV centres can have proactive...

Recommendations from the 36th Annual Meeting, Rome 2013
The working group discussed the scope and limits of pharmacovigilance (PV) centres in preventing medication errors and how PV centres can have proactive...

Recommendations from the 35th Annual Meeting, Brazil 2012
The working group discussed the scope and limits of pharmacovigilance (PV) centres in preventing medication errors and how PV centres can have proactive...

Recommendations from the 34th Annual Meeting, Dubrovnik 2011
The working group discussed the scope and limits of pharmacovigilance (PV) centres in preventing medication errors and how PV centres can have proactive...

Recommendations from the 33rd Annual Meeting, Accra 2010
The working group discussed the scope and limits of pharmacovigilance (PV) centres in preventing medication errors and how PV centres can have proactive...
