Hypertension
Providing continuum of care from early detection to control of hypertension and improving quality of care is a critical factor for leading a healthy life. It can also lead to decrease in morbidity and mortality due to CVDs.
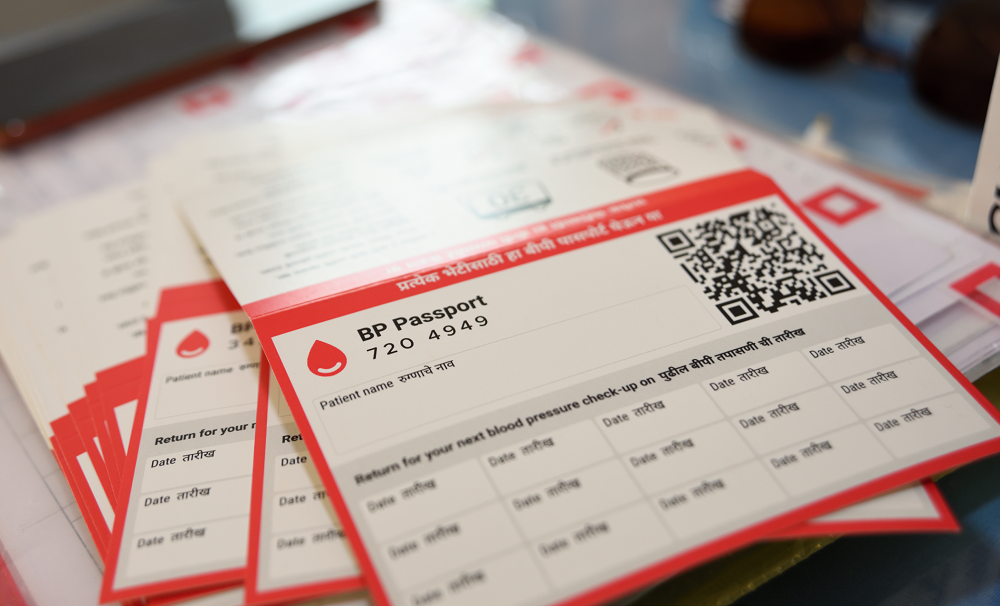
Measurement of blood pressure is quick and painless. Written as two numbers, the first (systolic) number represents pressure in blood vessels when the heart contracts or beats and second (diastolic) number represents pressure in the vessels when the heart rests between beats. Hypertension is diagnosed if, when measured twice on different days, systolic blood pressure on both readings is ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure on both readings is ≥90 mmHg. It is important to know one’s blood pressure reading by checking it regularly, adopting a healthy lifestyle and staying on prescribed treatment to reduce hypertension and its complications.
Nearly 63% of total deaths in India are due to noncommunicable diseases, of which 27% are attributed to cardiovascular disease which affects 45% people in the 40-69 age group. Raised blood pressure is among the most important risk factors for CVDs. Moreover, it remains poorly controlled due to low awareness about hypertension, lack of appropriate care through primary care and poor follow up.
India Hypertension Control Initiative(IHCI)
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD), which include heart attacks and strokes, are the most common cause of mortality and morbidity across the world and are responsible for one-third of total deaths in India. Uncontrolled blood pressure is one of the main risk factors for CVD. Of the estimated 220 million people in India living with hypertension, only 12% have their blood pressure under control. Hypertension kills more adults than any other cause and is readily preventable and treatable.
To strengthen hypertension treatment and control, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of India, in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research, WHO Country Office for India, State governments and Resolve to Save Lives (technical partner), launched the India Hypertension Control Initiative (IHCI) in November 2017. The initiative includes a standard hypertension-control programme approach drawn from the World Health Organization HEARTS technical package for cardiovascular disease management in primary health care.
By June 2022, IHCI marked a significant milestone and is being implemented in more than 110 districts across 23 states. More than 2.5 million patients with hypertension have been enrolled and on treatment across 16 000 + health facilities and are being followed up.
Technical links